Sitting: The New Smoking – A Silent Health Crisis
There’s a new epidemic in town, and it’s not what you might think. Sitting, often called “the new smoking,” has become a widespread health concern in modern society.
As technological advances make our lives more convenient and sedentary, we spend more time on our backsides than ever. The consequences of this shift are severe, with numerous studies linking prolonged sitting to a wide array of health problems.
Let’s examine why sitting has earned this alarming moniker and explore the impact of prolonged sitting on our health.
The Evolution of the Sedentary Lifestyle
Over the past few decades, our lifestyles have changed dramatically. Advances in technology have made many manual tasks obsolete, and we now spend most of our waking hours sitting. We sit at desks while working, on couches, watching TV, and in cars during our commutes. Even our leisure time is increasingly sedentary, with video games and social media dominating our free time. This shift has created a significant imbalance in our daily lives, causing our bodies to suffer the consequences.
The Research: Sitting and Health Risks
A growing body of research highlights the dangers of a sedentary lifestyle. According to multiple studies, sitting for long periods increases the risk of developing a wide range of health issues, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and even certain types of cancer.
A study published in the Lancet found that sitting for more than eight hours a day can increase the risk of premature death by up to 60%.
Not only does prolonged sitting affect our physical health, but it also impacts our mental well-being. Sedentary behavior has been linked to increased feelings of anxiety, depression, and lower overall life satisfaction.
How Sitting Affects the Body
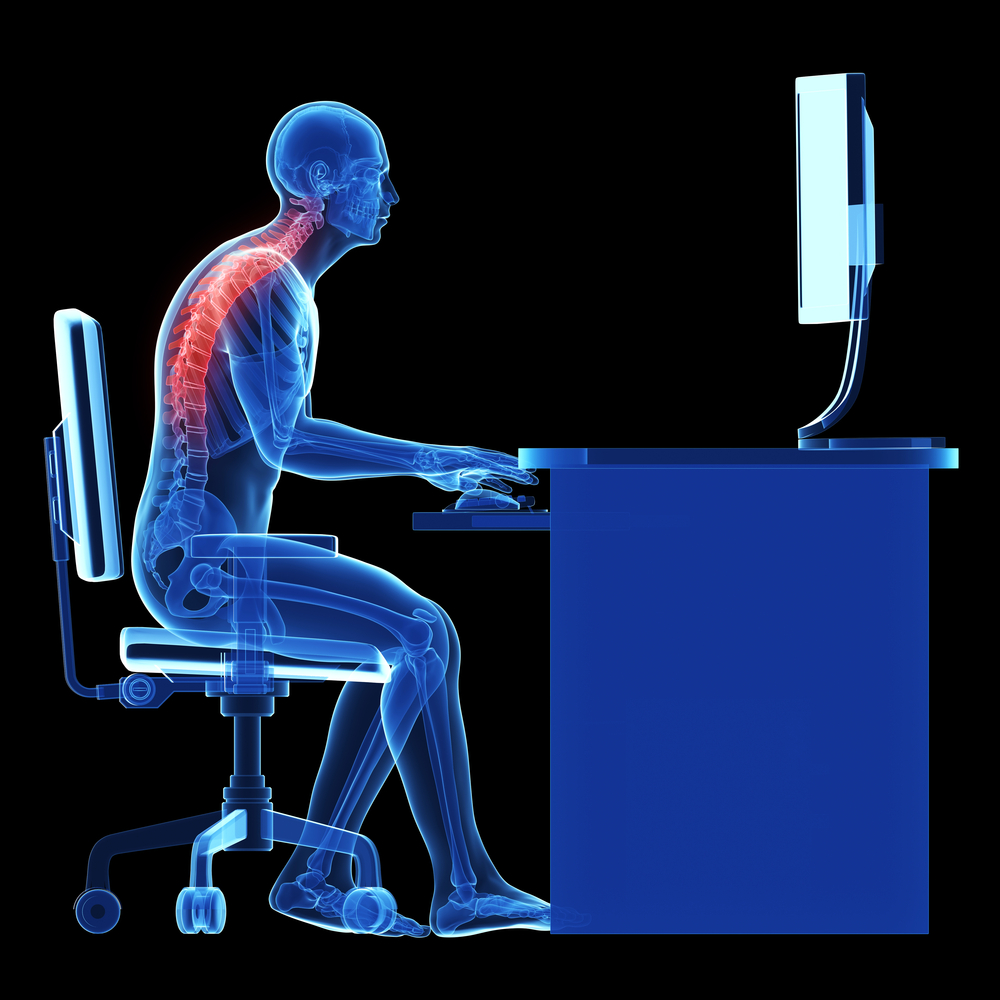
You might wonder how something as seemingly harmless as sitting could wreak such havoc on our bodies. When we sit, our muscles are inactive, leading to a decrease in calorie burning and a slowdown of our metabolism. This can result in weight gain and a higher likelihood of developing obesity-related health issues.
Moreover, sitting for extended periods causes our muscles to weaken and lose flexibility. This can lead to poor posture, back pain, and an increased risk of injury. Additionally, inactivity reduces blood flow, contributing to the development of blood clots and increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Sitting and the Workplace
The modern workplace is a significant contributor to our sedentary lifestyles. Many people spend 8-10 hours per day sitting at a desk, leading to a variety of health issues. Employers and employees alike need to recognize the dangers of prolonged sitting and take steps to minimize these risks.
There are several ways to combat the adverse effects of sitting in the workplace. One solution is a standing desk, which allows you to alternate between sitting and standing throughout the day. Additionally, taking regular breaks to stand up, stretch, and walk around can help break up long periods of sitting.
Another option is to promote a culture of workplace wellness. This can include offering fitness classes, incentivizing employees to exercise, and encouraging walking meetings instead of sitting in conference rooms.
The Role of Exercise
While exercise is essential for overall health, it’s important to note that even regular physical activity may only partially counteract the effects of prolonged sitting.
A study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that those who sit for eight or more hours per day and do not engage in moderate-to-vigorous exercise have a higher risk of developing heart disease.
However, incorporating exercise into your daily routine can still help mitigate the risks associated with sitting. Aim to get at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities two or more days a week.
Moreover, try to break up long periods of sitting by incorporating more movement throughout the day. For example, consider taking a short walk during your lunch break or standing up to stretch every hour.
These small changes can significantly affect your overall health and well-being.
Tips for Reducing Sedentary Behavior
Reducing the amount of time spent sitting can significantly improve your health. Here are some practical tips to help you combat sedentary behavior:
1. Set a reminder to stand up and move every hour. Use a smartphone or a smartwatch to help you remember to take regular breaks.
2. Stand while talking on the phone or watching TV. This simple change can help you burn more calories and improve your posture.
3. Take the stairs instead of the elevator whenever possible. Climbing stairs is a great way to increase your daily physical activity.
4. Use a fitness tracker to monitor your daily steps and set goals to increase your daily movement.
5. Incorporate more walking into your daily routine. For example, park farther away from your destination, or get off public transportation one stop earlier and walk the rest of the way.
6. Participate in active hobbies, such as gardening, hiking, or dancing, to increase your overall activity level.
7. Consider investing in a standing or adjustable desk to reduce the amount of time spent sitting at work.
8. Encourage friends and family to join you in your efforts to lead a more active lifestyle. Having a support system can make it easier to stick to your goals.
Get off your butt!
It’s essential to recognize the risks associated with a sedentary lifestyle and take proactive steps to incorporate more movement into our daily routines. By making simple changes, such as standing more often, taking regular breaks, and incorporating exercise into our lives, we can combat the dangers of sitting and improve our overall health and well-being.
Remember, small changes can significantly impact your health, so stand up and get moving.
Take care, even down there.
Share this Post